Choosing the right software is one of the most critical decisions a business can make. The choice between custom software and pre-built (off-the-shelf) software affects efficiency, costs, scalability, and long-term growth. While pre-built solutions offer speed and convenience, custom software provides tailored functionality that aligns perfectly with business needs. Understanding the advantages, limitations, and costs of each option helps businesses make an informed decision that maximizes value and supports strategic objectives. This guide breaks down the key differences and helps determine which solution is right for your organization. What Is Pre-Built Software? Pre-built software is a ready-made application designed for general use across a wide range of businesses. It is usually installed or accessed via subscription, with pre-defined features and workflows. These solutions are quick to deploy and often come with support and regular updates. However, they are built for general requirements, which means they may not fully meet your organization’s unique needs. Businesses may need to adapt processes to the software or rely on multiple tools to fill functional gaps. What Is Custom Software? Custom software is developed specifically for your business to meet its unique requirements. It is built to support your workflows, processes, and long-term objectives. Unlike pre-built software, custom solutions offer flexibility, scalability, and precise alignment with your operations. From automating internal processes to improving customer experiences, custom software is tailored to solve your specific challenges and grow with your business. Key Differences Between Custom and Pre-Built Software Understanding the differences between custom and pre-built software is crucial for making an informed decision. Each approach has unique advantages, costs, and limitations, and choosing the right one depends on your business needs, workflows, and long-term goals. 1. Functionality and Fit Pre-built software offers standard features designed to meet the needs of a wide range of businesses. While it can cover common tasks, it may not fully support your unique processes, forcing teams to adapt their workflows to the software. Custom software, on the other hand, is built specifically around your business operations. Every feature is designed to align with your workflows, ensuring the software truly supports your goals and maximizes efficiency. 2. Implementation Time Pre-built software is ready to use immediately, allowing businesses to deploy it within days or weeks. This makes it a convenient option when time is critical. Custom software requires a development cycle that includes requirement gathering, design, testing, and deployment. While this takes more time upfront, the result is a solution that fits your exact needs and avoids compromises on functionality. 3. Cost Structure Pre-built software generally comes with lower initial costs and often uses subscription-based pricing models. This makes it accessible for businesses with limited budgets. Custom software typically requires a higher upfront investment. However, it avoids unnecessary licensing fees for features you don’t use and provides better long-term value because it grows and adapts with your business. 4. Scalability Pre-built software may have limitations when it comes to customization or scaling as your business grows. Adding new features or accommodating more users can be difficult or expensive. Custom software is designed to scale with your organization. As your workflows evolve or your team grows, the software can be updated or expanded without major disruption, ensuring it remains useful for years to come. 5. Support and Maintenance With pre-built software, support is generally standardized, and updates are provided according to the vendor’s schedule. Customization options for these updates are limited. Custom software comes with tailored support and maintenance plans. Developers can address issues, add new features, and modify the software as your business needs change, ensuring your system stays efficient and relevant. Benefits of Pre-Built Software Pre-built software, also known as off-the-shelf software, offers several advantages for businesses that need ready-to-use solutions. While it may not be tailored to every workflow, it provides convenience, cost-effectiveness, and reliability that can be valuable for many organizations. Quick Deployment One of the main benefits of pre-built software is its speed of implementation. Since the application is already developed, businesses can get started immediately without long development cycles. This is particularly useful for teams that need a fast solution to manage operations, track data, or support day-to-day processes. Lower Upfront Costs Pre-built solutions generally come with lower initial expenses compared to custom software. Many offer subscription-based pricing or one-time purchase options, making them ideal for small businesses or startups with limited budgets. This allows organizations to access functional software without committing to a large upfront investment. Reliable Updates Most pre-built software providers regularly release updates, bug fixes, and enhancements. This ensures that the software remains compatible with evolving technology standards and reduces the burden of maintenance on your internal teams. Businesses can rely on vendor support for troubleshooting and technical issues. Proven Functionality Pre-built software has been tested by many users across industries, which reduces the risk of errors, bugs, or performance issues. Its functionality is established and reliable, giving businesses confidence that the core features will work effectively without extensive testing or customization. Benefits of Custom Software Custom software offers unique advantages for businesses that need solutions designed specifically for their workflows, processes, and long-term goals. Unlike pre-built software, it provides flexibility, scalability, and tailored functionality that helps organizations operate more efficiently and gain a competitive edge. Custom Functionality Custom software is built to meet your business’s specific requirements. Every feature is designed around your processes, eliminating unnecessary tools and ensuring that the software truly supports your operations. This precision allows teams to work more efficiently and reduces time wasted on tasks that generic software cannot handle. Better Integration Custom solutions connect seamlessly with your existing systems, tools, and databases. This ensures smooth data flow across platforms, reduces duplicate work, and allows teams to access all necessary information in one place. Better integration leads to fewer errors, faster processes, and improved decision-making. Scalable for Growth As your business grows, custom software can adapt to new workflows, additional users, or increased workloads. Unlike off-the-shelf solutions, which may have limitations, custom software evolves with your organization,
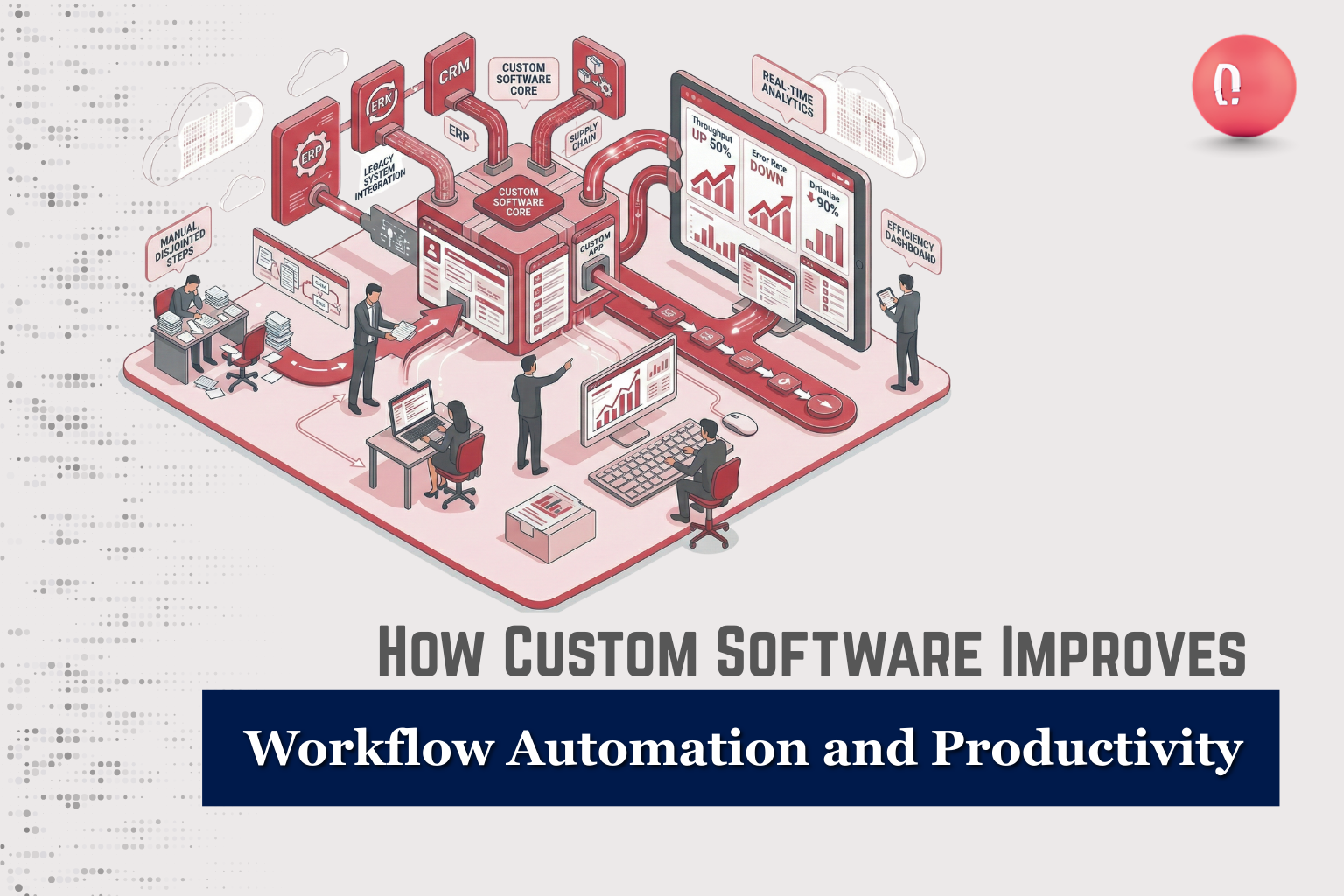
Modern businesses rely on efficient workflows to stay competitive and meet growing demands. Manual processes, disconnected tools, and repetitive tasks often slow teams down and increase the risk of errors. This is where custom software plays a critical role by automating workflows and improving productivity across the organization. Custom software is designed around how your business actually operates. Instead of forcing teams to adapt to generic systems, it simplifies daily tasks, connects processes, and allows employees to focus on meaningful work that drives results. What Is Workflow Automation? Workflow automation uses software to handle repetitive and rule based tasks with minimal human intervention. It ensures that processes move smoothly from one step to the next without delays or manual effort. With custom software, workflow automation is built specifically for your business processes. This ensures automation supports your goals rather than limiting how your teams work. Why Generic Tools Often Fall Short Generic or off-the-shelf software is designed to serve a wide range of businesses, which limits how well it fits specific workflows. While these tools usually offer basic automation features, they are built for general use rather than tailored business processes. As a result, they often include unnecessary features that add complexity while failing to support critical functions your teams rely on every day. Because generic tools are not aligned with how your business actually operates, employees are often forced to adjust their workflows or rely on manual workarounds. This reduces the effectiveness of automation and slows productivity instead of improving it. Poor alignment also makes adoption harder, as users may find the software confusing or inefficient for their tasks. Custom software solves these challenges by focusing only on what matters most to your business. It is designed around your workflows, automates the right processes, and removes unnecessary complexity. This alignment makes automation more effective, improves user adoption, and delivers long term productivity gains that generic tools cannot provide. How Custom Software Improves Workflow Automation Custom software transforms the way businesses manage daily operations by automating tasks and connecting processes. Instead of relying on manual effort, it creates structured workflows that improve speed, accuracy, and overall efficiency. Automates Repetitive Tasks Custom software can automate routine activities such as data entry, approvals, notifications, and reporting. By removing repetitive manual work, employees save time and can focus on more meaningful tasks. Automation also reduces the risk of human error and ensures that tasks are completed consistently and on schedule. Creates Seamless Process Flow Custom solutions connect different systems, teams, and departments into a single, unified workflow. When one task is completed, the next step is automatically triggered without manual intervention. This eliminates delays, improves coordination between teams, and ensures work moves smoothly from start to finish. Reduces Bottlenecks and Delays Workflow automation removes the need for constant follow ups and manual handoffs. Tasks progress automatically, approvals are completed faster, and projects remain on track. This helps businesses avoid unnecessary delays and maintain momentum without continuous supervision. Improves Accuracy and Consistency Automated workflows follow predefined rules every time, ensuring tasks are completed the same way on each execution. This consistency reduces mistakes, improves reliability, and maintains high quality standards across business operations. How Custom Software Boosts Productivity Custom software improves productivity by simplifying how teams work and removing unnecessary obstacles. By aligning technology with daily tasks, it helps employees work faster, collaborate better, and deliver consistent results as the business grows. Saves Time for Employees By handling repetitive and time consuming work, custom software allows employees to focus on strategic, creative, and high value tasks. This not only improves efficiency but also increases job satisfaction, as teams spend less time on manual work and more time contributing meaningfully to business goals. Enhances Collaboration Custom software can centralize communication, task management, and documentation in one platform. Teams gain better visibility into workflows, responsibilities, and progress, which reduces confusion and improves coordination across departments. Clear collaboration leads to faster execution and better outcomes. Provides Real Time Insights With custom dashboards and reporting tools, managers gain real time visibility into workflow performance and productivity. These insights help identify inefficiencies early, track progress accurately, and make informed decisions that improve overall operational efficiency. Scales with Business Growth As businesses grow, their workflows and workloads become more complex. Custom software can adapt to new requirements, support additional users, and handle increased demand without disrupting operations. This ensures productivity continues to improve without the need for major system changes or replacements. Common Workflow Automation Use Cases Workflow automation can be applied across multiple business functions to improve efficiency, accuracy, and employee experience. Custom software ensures automation is aligned with real operational needs rather than generic processes. Employee Onboarding and HR Processes Custom software can automate employee onboarding, leave approvals, and performance tracking. This reduces administrative workload for HR teams and ensures a smoother, more consistent experience for employees from their first day onward. Sales and Customer Management Custom workflows help automate lead tracking, follow ups, and customer communication. By reducing manual data entry and delays, sales teams can focus on building relationships, closing deals faster, and improving customer satisfaction. Finance and Operations Automation simplifies invoice processing, approvals, and financial reporting. This reduces delays, minimizes errors, and ensures greater accuracy in financial operations, helping businesses maintain better control over cash flow and compliance. Project and Task Management Custom tools ensure tasks are assigned clearly, progress is tracked in real time, and deadlines are met. Automation reduces the need for manual follow ups and keeps projects on schedule with minimal effort. Why Businesses Choose DLAN for Custom Workflow Automation DLAN designs custom software solutions that streamline workflows and improve productivity. Their team analyzes existing processes and builds automation that aligns with real business needs. With scalable, secure, and practical solutions, DLAN helps businesses reduce inefficiencies and maximize performance. Ready to automate your workflows and boost productivity?Contact DLAN today to explore custom software solutions designed for your business growth.
Technology is a critical driver of modern business growth. Choosing the right IT consultancy can have a lasting impact on efficiency, innovation, and long term success. With the right partner, businesses can align technology with strategic goals, avoid costly mistakes, and scale operations effectively. However, selecting the wrong consultancy can lead to wasted budgets, delayed projects, and missed growth opportunities. Finding the ideal IT consultancy requires careful evaluation of expertise, approach, and alignment with your business objectives. This guide explores the key factors to consider when choosing a consultancy that can support long term growth. 1. Assess Your Business Needs and Goals Before engaging a consultancy, clearly define your business objectives and technology requirements. Identify areas where your current IT systems are falling short or where strategic guidance is needed. Consider whether you need support for long term IT strategy, digital transformation, cybersecurity, cloud migration, or day-to-day operational challenges. A consultancy that understands your goals can tailor solutions that directly support growth rather than offering generic recommendations. Clear business objectives also help evaluate whether a consultancy’s services match your specific needs. 2. Look for Proven Expertise and Industry Experience Experience matters when choosing an IT consultancy. Look for a partner with a track record of successful projects in your industry or similar business environments. Expertise in areas like cybersecurity, cloud computing, IT infrastructure, and digital transformation is critical for long term growth. Consultancies with a broad range of experience can anticipate challenges, avoid common pitfalls, and recommend solutions that are scalable, secure, and efficient. Asking for case studies or client references can provide insight into their capability and reliability. 3. Evaluate Their Strategic Approach The right consultancy should focus on long term strategy, not just short term fixes. They should provide a structured approach to assessing your IT environment, identifying gaps, and developing a roadmap for growth. A strategic consultancy helps align technology investments with business objectives, ensuring every solution supports efficiency, scalability, and measurable outcomes. Avoid consultancies that focus solely on implementing tools without considering how they fit into your broader business strategy. 4. Check for Customized Solutions Every business is unique, and so are its technology needs. The consultancy you choose should offer tailored solutions that align with your industry, budget, and growth goals. Customized recommendations ensure better adoption, reduce unnecessary costs, and maximize return on investment. Avoid partners that rely on one-size-fits-all solutions, as these rarely address specific business challenges effectively. 5. Consider Communication and Collaboration Successful IT projects depend on clear communication and collaboration. The consultancy should provide transparent updates, explain technical concepts in understandable terms, and involve key stakeholders throughout the process. Strong collaboration ensures expectations are aligned, projects stay on schedule, and solutions are adopted effectively by your team. A consultancy that values partnership and proactive communication is more likely to deliver long term value. 6. Evaluate Flexibility and Scalability Businesses grow and evolve, and technology needs change accordingly. Choose a consultancy that can scale its services to match your growth trajectory. Whether you need ongoing advisory support, project-based assistance, or full IT strategy planning, a flexible consultancy adapts to changing requirements without disrupting operations or increasing costs unnecessarily. 7. Check References and Track Record Always ask for client references and case studies. Speaking with previous clients provides insight into the consultancy’s reliability, expertise, and ability to deliver on promises. A strong track record demonstrates their ability to handle complex projects and provide strategic value, reducing the risk of poor outcomes. 8. Understand Pricing and Value Cost is an important consideration, but it should not be the sole factor. Focus on the value provided relative to your business goals. Ensure the consultancy offers transparent pricing and clear deliverables. The right partner balances cost efficiency with long term strategic benefits, helping you achieve measurable growth without unexpected expenses. Why DLAN Is a Trusted IT Consultancy for Growth DLAN helps businesses achieve long term growth by aligning technology with strategic objectives. Their consultants provide tailored roadmaps, expert guidance, and practical solutions that support scalability, efficiency, and innovation. With a focus on measurable outcomes, DLAN ensures technology investments drive business performance and reduce unnecessary costs. Ready to plan your IT strategy for long-term growth?Contact DLAN today for a strategic IT consultation and start building a scalable, cost-effective technology roadmap.
Technology plays a critical role in how modern businesses operate, compete, and grow in today’s digital landscape. From daily operations to long term planning, organizations rely on technology to improve efficiency, communication, and decision making. However, when technology is adopted without a clear strategy, it often leads to wasted budgets, disconnected systems, and limited business impact. Strategic IT consulting helps bridge this gap by aligning technology decisions with real business objectives. Instead of focusing only on tools and systems, it ensures every technology investment supports growth, efficiency, and long term success. By creating a clear roadmap and prioritizing the right solutions, strategic IT consulting turns technology into a powerful driver of measurable business outcomes. What Is Strategic IT Consulting? Strategic IT consulting is a structured approach that focuses on long term planning rather than short term technical fixes. It helps businesses define how technology should support their overall objectives, operational needs, and future growth. Instead of reacting to problems, strategic consulting emphasizes proactive decision making and thoughtful technology investments. IT consultants work closely with leadership teams to understand business priorities, challenges, and goals. This collaboration ensures that technology decisions are aligned with the broader business strategy from the very beginning. As a result, organizations gain clearer direction, better resource utilization, and technology solutions that deliver lasting value. Why Aligning Technology with Business Goals Matters Aligning technology with business goals is essential for achieving efficiency, growth, and long term success. When technology supports clear objectives, it becomes a strategic asset rather than a cost burden. Improves Operational Efficiency When technology is aligned with business goals, teams can work faster and more effectively. Systems are designed to support workflows instead of creating obstacles. This reduces manual work, minimizes errors, and helps employees focus on high value tasks. Reduces Unnecessary Costs Misaligned technology often leads to overspending on tools that deliver little value. Businesses may invest in systems that overlap or do not support core objectives. Strategic alignment ensures budgets are spent on solutions that truly support business needs. Enhances Employee Experience Employees struggle when systems are complicated or poorly integrated. Aligned technology makes tools easier to use and improves daily work experiences. This leads to higher productivity, better collaboration, and increased job satisfaction. Supports Better Decision Making Technology aligned with business goals provides accurate and relevant data. This helps leaders make informed decisions based on real insights. Better data visibility supports planning, forecasting, and performance management. Enables Sustainable Business Growth Strategic alignment ensures technology can scale as the business grows. Systems are built to support future expansion without constant replacement. This creates a strong foundation for long term stability and competitive advantage. Key Steps in the Strategic IT Consulting Process Strategic IT consulting follows a structured process to ensure technology decisions support business objectives. Each step focuses on understanding business needs, planning the right solutions, and delivering measurable results. This approach helps organizations build a clear technology roadmap and achieve long term success. Understanding Business Objectives Before Technology Decisions Strategic IT consulting starts by understanding the business, not the technology. Consultants analyze company goals, processes, and pain points in detail. This helps identify where technology can create the biggest impact. It also prevents investing in tools that do not support business priorities. Creating a Clear IT Strategy and Roadmap An IT roadmap provides a clear plan for technology implementation and upgrades. Strategic consultants define priorities, timelines, and budget requirements. This roadmap helps businesses move forward in a structured and organized way. It ensures technology evolves alongside business growth and market changes. Improving Operational Efficiency Through Technology Strategic IT consulting focuses on improving efficiency across business operations. Consultants identify manual processes that can be automated or optimized. They recommend systems that reduce workload and improve productivity. This allows teams to focus more on strategic and revenue generating activities. Supporting Scalable Growth with the Right Technology Growing businesses need technology that can scale with increased demand. Strategic consultants design systems that support future expansion. They consider factors like performance, capacity, and flexibility. This ensures technology does not become a barrier to growth. Enhancing Collaboration and Communication Effective communication is essential for achieving business goals. Strategic IT consulting helps implement tools that improve collaboration across teams. These tools support remote work, file sharing, and real time communication. Better collaboration leads to faster decision making and improved outcomes. Strengthening Security While Supporting Business Needs Security should protect the business without slowing down operations. Strategic IT consultants balance security requirements with usability and productivity. They implement security measures that align with risk tolerance and compliance needs. This approach protects data while allowing teams to work efficiently. Optimizing IT Costs and Technology Investments Strategic consulting helps businesses spend wisely on technology. Consultants analyze existing systems and identify unnecessary expenses. They recommend cost effective solutions that meet business requirements. This improves return on investment and reduces wasted spending. Using Data and Analytics to Support Decision Making Data plays a key role in achieving business objectives. Strategic IT consulting helps businesses use data effectively. Consultants implement systems that provide accurate and actionable insights. This supports better planning, forecasting, and performance tracking. Managing Change and Technology Adoption Introducing new technology requires proper change management. Strategic consultants help plan adoption and training programs. They ensure employees understand and accept new systems. This reduces resistance and improves overall success. Measuring Technology Performance Against Business Goals Strategic IT consulting includes continuous evaluation and improvement. Consultants define metrics to measure technology performance and business impact. They review results and recommend adjustments when needed. This ensures technology continues to support evolving business goals. Why DLAN Is a Trusted Strategic IT Consulting Partner DLAN helps businesses align technology with their strategic objectives by focusing on real business needs. Their consultants take the time to understand your goals, challenges, and operational requirements before recommending solutions. With a structured approach, DLAN delivers clear IT roadmaps, expert guidance, and practical implementation support. This ensures every technology decision drives measurable results and long term business value. Ready to align your
Growing businesses often face IT challenges that slow down progress and reduce productivity.These issues can impact employees, customers, and overall business performance.IT consultants help identify problems early and provide solutions that support growth.Their experience and strategy help businesses scale without breaking their systems. 10 Common IT Challenges Growing Businesses Face As businesses grow, their IT systems often struggle to keep up with new demands. These challenges can lead to downtime, security risks, and inefficient operations. Below are the 10 most common IT issues growing businesses face and how consultants solve them. 1. Outdated Technology and Infrastructure Many growing businesses rely on old hardware and software that no longer performs well. Outdated systems cause slow performance, frequent crashes, and frustrated employees. IT consultants evaluate your infrastructure and recommend upgrades based on your needs. They help you plan upgrades in phases to avoid downtime and disruption. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants start with a full technology audit to assess your current systems. They identify outdated hardware, software, and network components that need upgrading. Then they create a phased plan to update systems without interrupting business operations. This ensures your technology supports growth and improves overall efficiency. 2. Limited IT Staff and Expertise Growing businesses often lack skilled IT professionals to manage their expanding systems. Small teams struggle to handle network issues, security, and user support. IT consultants fill this gap by providing expert guidance and strategic planning. They work as an extension of your team and support your technology needs. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants provide access to specialized IT skills without hiring full time staff. They help manage complex projects such as cloud migration and network upgrades. They also train your staff to handle basic IT tasks and improve internal skills. This reduces workload on your team and ensures tasks are handled efficiently. 3. Security Risks and Vulnerabilities Security threats are growing every year, especially for businesses with valuable data. Small and mid sized businesses are often targeted due to weak security measures. IT consultants assess your security posture and identify vulnerabilities in your systems. They help implement strong security controls to protect your data and network. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants perform security assessments and penetration testing to find weaknesses. They implement firewalls, access controls, and data encryption based on your needs. They also create security policies and training programs for your employees. This reduces the risk of data breaches and protects your business reputation. 4. Lack of Standardized IT Processes Many growing businesses have inconsistent IT processes and unclear policies. This leads to confusion, mistakes, and slow response to technical issues. IT consultants help establish standardized IT processes and best practices. This improves efficiency and ensures consistent performance across teams. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants create clear IT policies for device management, access, and security. They define standard operating procedures for troubleshooting and support requests. They also set guidelines for software installation and data backup practices. Standard processes help your business run smoothly and reduce technical errors. 5. Inefficient Data Management Growing businesses generate more data, and managing it becomes challenging quickly. Poor data management leads to inaccurate reporting and decision making. IT consultants help organize data systems and improve data storage processes. They also implement systems that allow easy access and better reporting. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants assess your data systems and identify gaps in storage and reporting. They recommend data management solutions that fit your business needs and budget. They also help integrate systems to ensure data flows accurately across platforms. This improves reporting accuracy and supports better business decisions. 6. Poor Network Performance and Connectivity Network issues are common in growing businesses with more users and devices. Slow network performance affects productivity and causes delays in daily tasks. IT consultants evaluate your network and identify performance bottlenecks. They recommend solutions to improve speed, reliability, and scalability. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants design a network that supports your current and future business needs. They upgrade network equipment and improve connectivity for all locations. They also implement monitoring tools to detect issues before they impact users. This ensures stable performance and reduces downtime across the organization. 7. Challenges with Remote Work and Collaboration Remote work is now a standard part of business operations. Many growing businesses struggle to provide secure and reliable remote access. IT consultants help implement tools and systems for remote collaboration and security. They ensure employees can work efficiently from anywhere without risk. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants set up secure remote access systems such as VPN and cloud tools. They also implement collaboration platforms that support communication and file sharing. They provide training to employees on best practices for remote work. This improves productivity and ensures secure remote operations for your business. 8. Difficulty Scaling IT with Business Growth When businesses grow, their IT systems must scale quickly and efficiently. Many companies struggle to scale because their systems were not designed for growth. IT consultants plan scalable solutions that support future expansion and demand. They ensure your IT infrastructure can handle growth without disruptions. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants analyze your business growth plans and future technology needs. They design scalable systems that can expand with your business over time. They also create a roadmap for gradual upgrades and improvements. This ensures your IT environment remains stable and supports long term growth. 9. Compliance and Regulatory Challenges Businesses in regulated industries must meet strict compliance requirements. Failure to comply can lead to penalties and damage to your reputation. IT consultants help businesses meet compliance standards and maintain security. They also help document processes and prepare for audits. How Consultants Solve This Challenge Consultants assess compliance requirements based on your industry and location. They implement policies and controls to meet regulatory standards. They also create documentation and prepare your team for audits and reviews. This reduces the risk of penalties and ensures your business follows best practices. 10. Difficulty Choosing the Right Technology Growing businesses
IT consultancy helps businesses plan, implement, and manage technology solutions for better performance and growth. A consultant evaluates your current IT environment and suggests improvements based on your business goals. They act as trusted advisors, helping you make informed decisions about technology investments and strategies. IT consultancy is not just about fixing issues; it is about aligning technology with business outcomes. What Is IT Consultancy? IT consultancy is a professional service that guides organizations on technology planning and implementation. It helps businesses make smart decisions, reduce risk, and improve efficiency in their IT operations. Consultants bring experience from multiple industries and understand the best practices that work. They help you avoid common mistakes and implement systems that support long term success. Definition and Core Purpose The core purpose of IT consultancy is to bridge business needs with technology solutions. Consultants evaluate your current systems and create a plan to improve performance and security. They help you identify gaps, risks, and opportunities for optimization in your IT environment. A good consultant ensures your technology supports your goals and not just your daily operations. How IT Consultancy Differs from IT Support IT support mainly handles day to day technical issues and user problems. IT consultancy focuses on strategy, planning, and long term improvements for the entire business. Support teams fix problems, while consultants design systems that prevent issues from happening. Consultancy is more about transformation, while support is about maintenance and troubleshooting. Key Services Offered by IT Consultants IT consultants offer a wide range of services, tailored to your business needs and industry. These services are designed to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and strengthen security. Consultants also help businesses adopt new technologies without disrupting their operations. Here are the main services offered by IT consultancy firms today. IT Strategy and Roadmap Planning Consultants create a strategic plan to align technology with your business goals. They develop a roadmap that outlines priorities, timelines, and budget requirements. This roadmap helps you make consistent progress without wasting resources. It also ensures your IT investments deliver measurable business results. Infrastructure Assessment and Optimization Consultants evaluate your network, servers, and hardware to identify performance gaps. They recommend upgrades, replacements, or optimization strategies based on your needs. This service improves system reliability and reduces downtime for your business. It also helps you get the most value from your existing technology investments. Network Design and Implementation IT consultants design secure and scalable network solutions for your organization. They ensure your network can support your growth and future technology needs. This includes network architecture, connectivity, and performance optimization. Proper network design reduces bottlenecks and improves communication across teams. Cloud Migration and Management Cloud migration helps businesses become more flexible and cost efficient. Consultants guide the process from planning to deployment and ongoing management. They help you choose the right cloud model for your business requirements. This ensures your cloud systems remain secure, scalable, and reliable. Security and Compliance Consulting Security is a major focus for every business, especially those handling sensitive data. IT consultants assess risks and implement security measures to protect your systems. They also help businesses meet compliance requirements and industry standards. This service reduces the chances of data breaches and legal penalties. Software and Systems Integration Many businesses struggle with multiple software systems that do not communicate well. Consultants help integrate systems to improve workflow and data accuracy. They ensure your software works together smoothly and supports your processes. This reduces manual work, errors, and improves overall productivity. IT Cost Optimization and Vendor Management Consultants analyze your IT spending and suggest ways to reduce costs without losing quality. They also manage vendor relationships and negotiate better terms on your behalf. This helps businesses save money and maintain strong technology performance. It also allows your team to focus on core business activities instead of vendor issues. What Does an IT Consultant Actually Do? An IT consultant performs multiple tasks to support your business transformation goals. They work closely with stakeholders to understand your challenges and objectives. Consultants analyze your systems, recommend improvements, and help with implementation. Their role is to guide your business through change while reducing risk and downtime. Business Needs Assessment Consultants begin by understanding your business processes, goals, and pain points. They meet with key stakeholders to gather information and evaluate needs. This assessment helps them identify what technology will best support your growth. It also helps them recommend solutions that fit your budget and timeline. Technology Audit and Gap Analysis A technology audit evaluates your existing systems, infrastructure, and security measures. Consultants identify gaps that may affect performance, security, or compliance. This analysis provides a clear picture of what needs to be improved or upgraded. It helps businesses make better decisions based on real data and expert insights. Solution Recommendations Consultants recommend technology solutions that match your business goals and budget. They present options with pros, cons, and implementation timelines. This helps businesses choose the best technology path without confusion. Recommendations are based on experience, best practices, and future trends. Implementation and Project Management Consultants manage the implementation process to ensure it is smooth and timely. They coordinate with your team and vendors to avoid disruptions in operations. Project management helps keep the process on track and within budget. It also ensures the solution is delivered correctly and meets business expectations. Ongoing Monitoring and Support Consultants provide ongoing support to monitor performance and fix issues quickly. They also recommend improvements as your business grows and needs change. This ensures your technology remains reliable and aligned with your goals. Continuous monitoring prevents small issues from turning into major problems. Signs Your Business Needs IT Consultancy Every business faces technology challenges at some point, and consultancy helps solve them. Here are clear signs that your organization needs professional IT consulting services. Frequent IT Downtime or System Failures If your systems crash often, your business productivity will drop significantly. Consultants can identify the root cause and implement long term fixes. They improve system stability, reduce downtime,
Technology has become one of the most important drivers of modern business growth. Yet many organizations still approach it tactically—hiring developers to build features, launch platforms, or complete short-term projects. While this approach may deliver software, it often fails to deliver sustainable business impact. This is why successful organizations no longer look for just a development team. They look for a technology partner—a team that understands business strategy, long-term scalability, and the real-world implications of technical decisions. At DLan, we work as that partner. Development Delivers Code — Partnership Delivers Outcomes A development team focuses on executing tasks. A technology partner focuses on achieving outcomes. When businesses work only with developers, projects are typically judged by whether features were delivered on time. When they work with a technology partner, success is measured by whether the solution improves operations, supports growth, and remains effective over time. DLan approaches every engagement with this mindset. We don’t just ask what needs to be built—we ask why it needs to exist, how it will be used, and how it must evolve as the business grows. Why Project-Based Technology Often Becomes a Liability Many organizations experience frustration after launching new systems. Software that initially seemed successful starts to feel rigid, expensive to maintain, or misaligned with evolving business needs. This usually happens because the technology was built to solve a momentary problem rather than support a long-term vision. Without architectural planning, data strategy, and scalability in mind, technology quickly turns into technical debt. DLan helps businesses avoid this trap by designing systems that anticipate change instead of reacting to it. A Business-First Approach to Technology Design At DLan, technology decisions always start with the business. Before writing code, we take time to understand how your organization operates, where inefficiencies exist, how decisions are made, and what growth looks like over the next several years. This context allows us to design solutions that support real workflows rather than theoretical ones. The result is technology that fits naturally into your organization instead of disrupting it. Building for Growth, Not Just Launch Launching software is only the beginning. Real value comes from how well that technology performs as usage grows, data increases, and business priorities shift. DLan builds with scalability in mind—ensuring systems remain stable, adaptable, and cost-effective as demands increase. This long-term thinking reduces rework, prevents performance issues, and allows businesses to grow without constantly rebuilding their technology stack. Supporting Change, Not Resisting It Change is inevitable. New markets, new customers, new regulations, and new opportunities all require technology to adapt. As a technology partner, DLan supports businesses beyond initial delivery. We help evolve platforms, enhance functionality, improve performance, and introduce automation or analytics as needs change. This ongoing partnership ensures technology remains an asset rather than an obstacle. Clear Communication Between Business and Technology One of the most common challenges in technology initiatives is misalignment between technical teams and business stakeholders. When communication breaks down, projects slow, expectations shift, and results suffer. DLan bridges this gap by translating business goals into technical strategy and technical decisions back into business impact. This clarity reduces risk, improves collaboration, and leads to better outcomes for everyone involved. Who Benefits Most From a Technology Partner Organizations that view technology as a strategic investment benefit the most from partnership. This includes businesses that rely heavily on software, data, and digital systems to operate efficiently or scale effectively. For these organizations, choosing a partner like DLan means gaining guidance, accountability, and long-term support—not just development capacity. Why Businesses Choose DLan Businesses choose DLan because we combine technical expertise with strategic thinking. We take ownership of outcomes, design for the future, and stay engaged beyond delivery. Our focus is not just on building systems, but on helping organizations operate smarter and grow stronger through technology. Choose Technology That Grows With You If your organization is ready to move beyond transactional development and build technology with long-term value, a partnership approach matters. DLan is ready to be that partner. Visit dlan.ai to start building technology that supports your business today—and adapts with you tomorrow.
Technology has become the backbone of modern businesses, supporting everything from daily operations to long term strategic growth. Organizations rely on IT systems to manage processes, ensure security, and maintain seamless communication across teams. As businesses scale, the complexity of their technology needs increases, making IT management a critical factor in maintaining efficiency and competitiveness. Deciding how to handle IT is one of the most important financial decisions for growing companies. Many organizations face the choice between building a full in house IT team or leveraging external IT consulting services. Each option comes with distinct advantages, challenges, and costs, which can significantly impact budgets, operational efficiency, and the ability to scale effectively. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with both business goals and financial strategy. Understanding In House IT Teams An in house IT team is composed of employees who are fully dedicated to managing a company’s technology. These teams handle day to day support, system maintenance, and resolving internal technical issues. Having an internal team provides direct control and ensures familiarity with the company’s processes and systems. However, building and maintaining a full time IT team can become expensive, especially for growing businesses with evolving technology needs. Costs Associated with In House IT Managing an in house IT team involves more than just hiring staff. Businesses must invest in salaries, tools, training, and infrastructure, while also preparing for unexpected operational challenges. Understanding these costs helps organizations make informed decisions about IT management and budgeting. Salaries and Benefits Maintaining an in house IT team requires significant investment in salaries and benefits. Businesses must offer competitive compensation packages to attract and retain skilled professionals. In addition to salaries, benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave add to the overall cost of keeping an internal team. Tools, Software, and Infrastructure An in house IT team also requires access to the right tools, software, and infrastructure. Businesses need to invest in software licenses, hardware upgrades, and network equipment to ensure smooth operations. These investments are ongoing, as systems require regular updates and maintenance to stay current with business needs. Ongoing Training and Skill Development As technology continues to evolve, IT staff must continuously update their skills through training programs. Ongoing training ensures that employees can manage modern systems, implement new solutions, and address emerging security threats. Without proper training, businesses risk inefficiencies and increased vulnerability. Operational Risks and Hidden Costs Unexpected absences, staff turnover, or skill gaps can disrupt daily IT operations. These disruptions may delay critical projects and increase costs for the organization. Businesses must also plan for contingencies to prevent downtime, which adds hidden expenses beyond salaries and infrastructure. Limitations of In House IT While having an in house IT team offers certain advantages, it also comes with several limitations that can impact efficiency and growth. Understanding these drawbacks helps businesses evaluate whether an internal team alone is sufficient for their technology needs. Limited Specialized Expertise In house teams may not always have deep expertise in specialized areas such as cybersecurity, cloud strategy, or advanced infrastructure. These gaps can prevent organizations from implementing cutting edge solutions or responding effectively to emerging security threats. Without access to specialized skills, businesses may miss opportunities to optimize their technology environment. Focus on Daily Operations Internal IT staff often spend the majority of their time managing day to day tasks such as troubleshooting, system maintenance, and user support. This focus on operational issues leaves little time for strategic planning, long term projects, or proactive improvements that could drive business growth. Resource Constraints for Major Projects Limited team size and resources can slow down the execution of large technology projects, system upgrades, and innovation initiatives. Businesses may face delays or incomplete implementations due to insufficient manpower or expertise within the internal team. Impact on Efficiency and Costs Over time, these limitations can lead to inefficiencies, project delays, and higher overall costs. Businesses may need to hire external experts for complex projects or incur additional expenses to train staff, increasing operational overhead. What Is IT Consulting? IT consulting gives businesses access to external experts who provide guidance on technology decisions and strategy. Consultants focus on planning, implementing, and optimizing technology solutions to meet specific business objectives. They can work on short term projects, such as system upgrades, or provide ongoing advisory support for long term planning. This model offers flexibility and access to specialized expertise without the costs and commitment of maintaining full time IT staff. Costs Associated with IT Consulting Understanding the costs of IT consulting helps businesses make informed decisions about how to manage their technology needs. Unlike in house IT, consulting offers flexibility and access to specialized expertise without long term financial commitments. Project-Based or Service-Based Fees IT consulting costs are usually structured around specific projects or services. Businesses pay for the work completed, such as implementing a new system, upgrading infrastructure, or providing advisory support. This structure allows companies to avoid paying for unused hours or resources, making IT spending more efficient and targeted. Pay Only for the Expertise You Need One of the main advantages of IT consulting is that you only pay for the level of expertise your business requires. Whether you need guidance for a single project or support for complex IT initiatives, consultants provide specialized skills that might be too costly or difficult to maintain in an internal team. No Long Term Salary or Benefits Unlike hiring full time IT staff, consulting does not involve salaries, health benefits, or retirement contributions. This eliminates the financial and administrative burden of long term employee commitments, allowing businesses to access expert knowledge without adding overhead. Predictable and Controllable Expenses IT consulting allows businesses to forecast costs more accurately because fees are agreed upon in advance. This predictability helps companies plan budgets, reduce unexpected expenses, and maintain control over IT spending. Businesses can scale consulting services up or down based on current needs, making this a flexible and cost effective solution. Benefits of
Operational inefficiency is one of the most common barriers to business growth. As organizations expand, processes become more complex, teams rely on manual workarounds, and systems fail to communicate effectively. Over time, this leads to wasted time, higher costs, and slower decision-making. At DLan, we help businesses address these challenges by designing smart, integrated technology solutions that streamline operations and improve performance across the organization. Why Inefficiency Grows as Businesses Scale Many operational inefficiencies are not caused by people — they are caused by systems. Tools that worked during early growth stages often become limiting as workloads increase and processes evolve. Disconnected platforms, duplicated data entry, and manual approvals create friction that slows teams down. Without the right technology foundation, even experienced teams struggle to operate efficiently. DLan focuses on eliminating these structural issues at the system level. Technology as a Driver of Operational Clarity When systems are designed correctly, they provide clarity rather than complexity. DLan helps businesses create technology environments where information flows smoothly between departments, processes are clearly defined, and teams have immediate access to the data they need. This clarity reduces errors, improves accountability, and allows employees to focus on meaningful work instead of repetitive tasks. Automating Processes Without Losing Control Automation is often misunderstood as replacing human involvement. In reality, effective automation supports teams by handling repetitive, rule-based tasks while keeping humans in control of critical decisions. DLan designs automation solutions that fit naturally into business workflows, reducing manual effort without sacrificing oversight. This approach improves consistency and efficiency while maintaining flexibility. Eliminating Data Silos Across the Organization Data silos are a major source of inefficiency. When information is spread across multiple systems, teams waste time reconciling data instead of using it. DLan helps businesses consolidate data into unified systems, ensuring everyone works from a single source of truth. This improves collaboration, reduces reporting delays, and enables faster, more accurate decision-making. Improving Decision Speed Through Better Systems Slow decisions often stem from slow access to information. When leaders lack visibility into real-time performance, they are forced to rely on assumptions rather than facts. DLan builds systems that provide timely, relevant insights, allowing businesses to respond quickly to issues and opportunities. Faster decisions lead to better outcomes and stronger operational control. Designing Systems That Support Daily Operations Technology should support how teams work every day — not add friction. DLan designs systems around real operational workflows, ensuring technology enhances productivity instead of disrupting it. This user-focused approach improves adoption and ensures long-term value. Long-Term Efficiency Through Scalable Design Short-term fixes may solve immediate problems, but they often create future inefficiencies. DLan focuses on building scalable systems that maintain efficiency as the business grows. By anticipating future demands, we help organizations avoid repeated rework and maintain consistent performance over time. Who Benefits Most From Operational Optimization Businesses that rely on complex processes, data-driven operations, or growing teams benefit most from technology-driven efficiency improvements. For these organizations, reducing operational friction directly impacts profitability, employee satisfaction, and customer experience. Why Businesses Choose DLan Organizations choose DLan because we focus on practical efficiency, measurable improvement, and long-term stability. Our solutions are designed to simplify operations, reduce waste, and help businesses operate at their best. Build Smarter, More Efficient Operations If your organization is struggling with inefficiencies, disconnected systems, or manual processes, technology can provide the clarity and control you need. DLan helps businesses streamline operations through smart, scalable technology. Visit dlan.ai to learn how we can help your business operate more efficiently and grow with confidence.
In today’s fast-moving digital world, businesses don’t just need technology — they need technology that delivers results. Generic tools, disconnected systems, and static reports often slow teams down instead of helping them grow. That’s where DLan stands apart. At dlan.ai, we help organizations transform data, software, and infrastructure into powerful digital ecosystems that support smarter decisions, operational efficiency, and long-term scalability. Why One-Size-Fits-All Technology No Longer Works Many businesses rely on off-the-shelf software that was never designed for their workflows, data structure, or growth plans. Over time, this leads to: DLan solves this by designing custom technology solutions that align precisely with how your business operates — today and tomorrow. Custom Software Built Around Your Business At the core of DLan’s services is custom software development. We don’t force your business to adapt to technology — we build technology that adapts to you. Our software solutions are designed to: From internal platforms to customer-facing systems, DLan delivers software that becomes a competitive advantage, not a limitation. Big Data & Advanced Analytics for Smarter Decisions Data is only valuable when it leads to action. DLan helps organizations unlock the full power of their data through big data engineering and advanced analytics, enabling teams to: Instead of relying on assumptions, your teams gain clarity backed by real insights. Real-Time Dashboards & Business Intelligence Traditional reports arrive too late to matter. Modern businesses need visibility as things happen, not after the fact. DLan builds real-time dashboards and business intelligence solutions that: Whether for executives or operational teams, these dashboards turn raw data into clear direction. End-to-End Digital Solutions — Not Just Development DLan is more than a development partner. We support clients across the full technology lifecycle: This end-to-end approach ensures that every solution delivers measurable business impact — not just technical completion. Industries We Support DLan’s solutions are designed to adapt across industries, including: If your business depends on data, software, or intelligent decision-making, DLan can help you move faster and smarter. What Makes DLan Different Clients choose DLan because we focus on: We build systems that work in the real world — under real business pressure. Ready to Build Technology That Works for You? If you’re looking to: DLan is ready to help. Visit dlan.ai and start building digital solutions that actually move your business forward.
- 1
- 2